
Food poisoning is a common health condition caused by consuming contaminated food or water. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins produced by these microorganisms. The symptoms of food poisoning range from mild to severe and can include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, and abdominal pain.
Causes of Food Poisoning

- Bacteria: The most common cause of food poisoning is bacteria such as Salmonella, Campylobacter, and E. coli. These bacteria can be found in raw meat, poultry, eggs, and unpasteurized milk. They can also be found on fruits and vegetables that have been contaminated by animal feces or contaminated water.
- Viruses: Norovirus and hepatitis A are two common viruses that can cause food poisoning. Norovirus is often spread by food handlers who have not washed their hands properly, while hepatitis A is usually spread through contaminated water or food.
- Parasites: Parasites such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium can be found in contaminated water or food. These parasites can cause food poisoning and other health problems.
- Toxins: Toxins produced by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus cereus can cause food poisoning. These toxins can be produced in food that has been left at room temperature for too long or not cooked properly.
Symptoms of Food Poisoning
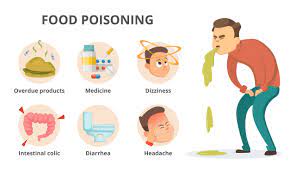
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- Headache
- Dehydration
Prevention of Food Poisoning
The best way to prevent food poisoning is to take steps to ensure that your food is properly cooked, stored, and handled. Here are some tips to help prevent food poisoning:

- Wash your hands: Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after handling food.

- Cook food properly: Cook meat, poultry, and eggs thoroughly to kill any bacteria that may be present.

- Store food properly: Store food at the appropriate temperature to prevent the growth of bacteria. Keep hot food hot and cold food cold.
- Avoid cross-contamination: Use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw meat, poultry, and fish to avoid cross-contamination.
- Avoid risky foods: Avoid eating raw or undercooked meat, poultry, and fish. Also, avoid unpasteurized milk and cheese.
While prevention is the best approach to dealing with food poisoning, there are modern methods to treat this condition. Some of the modern methods to treat food poisoning:

- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are often used to treat bacterial infections that cause food poisoning. They work by killing the bacteria or stopping their growth. However, not all cases of food poisoning require antibiotics, and their use should be determined by a healthcare professional.

- Probiotics: Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are good for your digestive system. They can help replenish the good bacteria in your gut that may have been destroyed by food poisoning. Probiotics can be found in supplements and certain foods like yogurt and kefir.

- Rehydration: Rehydration is an important part of treating food poisoning. When you have food poisoning, you lose a lot of fluids due to vomiting and diarrhea. It is important to drink plenty of fluids, including water, clear broths, and electrolyte-rich drinks like sports drinks or coconut water. In severe cases, intravenous fluids may be needed.

- Antiemetics: Antiemetics are medications that can help control nausea and vomiting. They are often used to treat the symptoms of food poisoning, especially if they are severe. Antiemetics can be taken orally or given intravenously.

- Antidiarrheals: Antidiarrheals are medications that can help control diarrhea. They are often used to treat the symptoms of food poisoning, especially if they are severe. Antidiarrheals can be taken orally or given intravenously.

- Activated charcoal: Activated charcoal is a type of charcoal that has been treated with oxygen to make it highly porous. It can bind to toxins in the gut and prevent their absorption into the body. Activated charcoal can be taken orally in pill or powder form.
While medical treatment may be necessary in severe cases, there are several home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms of food poisoning. Here are some of the best home remedies to treat food poisoning:
- Hydration: One of the most important things you can do to treat food poisoning at home is to stay hydrated. Vomiting and diarrhea can cause dehydration, which can make your symptoms worse. Drink plenty of water, clear broths, and other fluids to replenish lost fluids and electrolytes.

- Ginger: Ginger is a natural anti-inflammatory and anti-nausea agent. It can help soothe an upset stomach and alleviate nausea and vomiting. You can consume ginger in various forms such as ginger tea, ginger ale, or ginger candies.

- Apple cider vinegar: Apple cider vinegar has antimicrobial properties that can help kill the bacteria or viruses that are causing food poisoning. Mix one to two tablespoons of apple cider vinegar with a glass of water and drink it to help alleviate your symptoms.

- Bananas: Bananas are a good source of potassium, which can be lost during bouts of vomiting and diarrhea. They are also easy to digest, making them a good food to eat when you have food poisoning.

- Peppermint: Peppermint has a calming effect on the digestive system and can help alleviate nausea and stomach cramps. You can consume peppermint in various forms such as peppermint tea or peppermint oil capsules.

- BRAT diet: The BRAT diet stands for bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast. This diet consists of bland foods that are easy to digest and can help alleviate symptoms of food poisoning. The BRAT diet is recommended for a few days until your symptoms improve.

- Rest: Rest is an important part of treating food poisoning. Your body needs time to recover from the infection, so make sure you get plenty of rest and avoid strenuous activities.
Conclusion
Food poisoning can be a painful and uncomfortable condition, but there are several home / modern remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms. If your symptoms are severe or do not improve, seek medical attention immediately.
